Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves moving hair follicles from a donor site (usually the back or sides of the scalp) to areas where hair is thinning or completely bald. This procedure is most commonly used to treat male pattern baldness, but it can also be used for women experiencing hair loss, especially those with thinning hair. There are two primary methods for hair transplantation: FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation) and FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction).
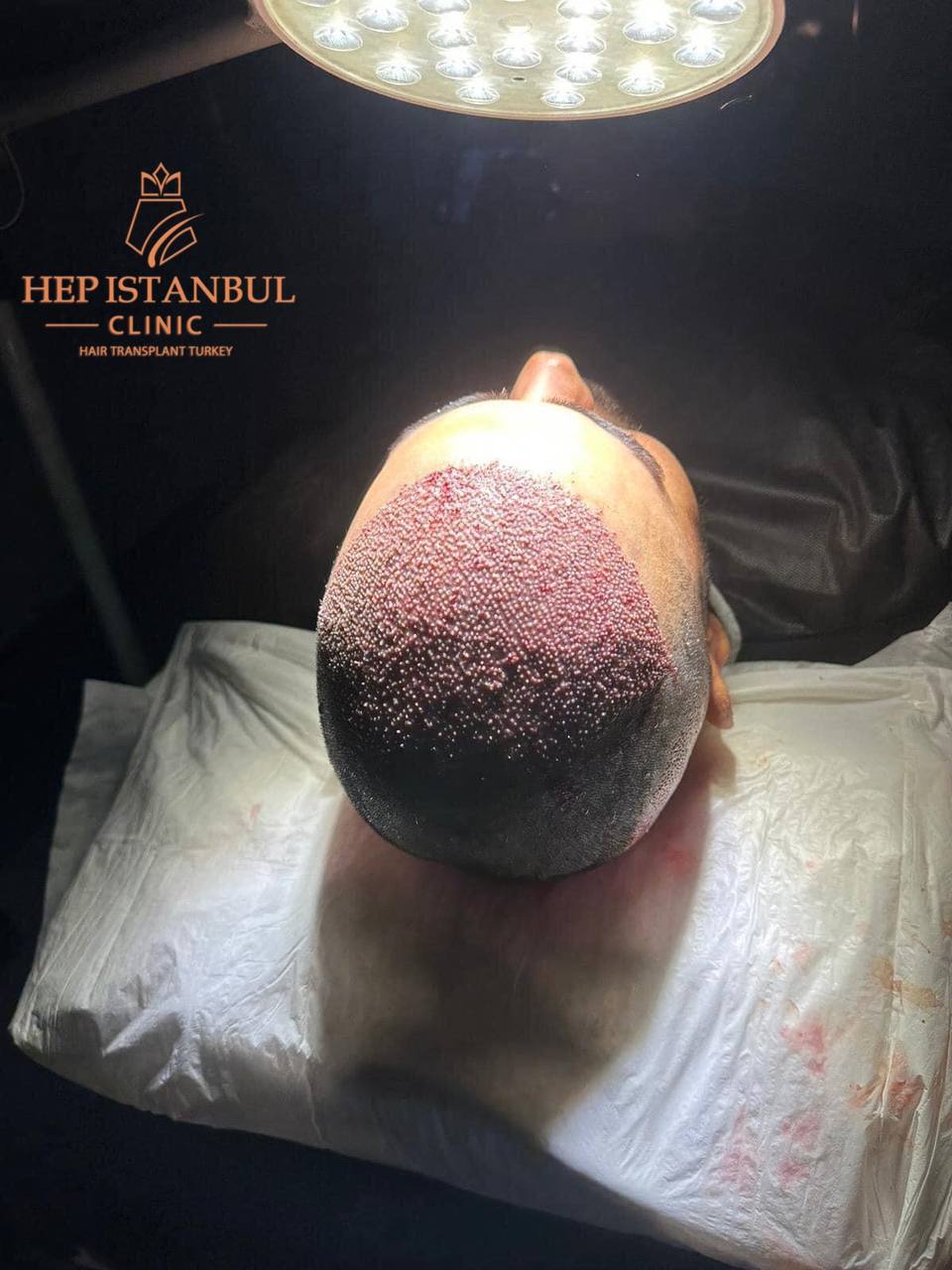
In FUT, a strip of scalp is removed from the donor site, and individual hair follicles are dissected and transplanted into the bald area. In contrast, FUE involves extracting hair follicles individually using a small punch device, without the need for a scalpel. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, but FUE is generally less invasive with no visible linear scar, whereas FUT can offer more grafts in a single session but leaves a linear scar
Hair transplantation is a permanent solution to hair loss, and the transplanted hair is typically resistant to DHT (dihydrotestosterone), the hormone that causes hair loss. The procedure is minimally painful, with most patients returning to their normal routine within a few days after the surgery.
